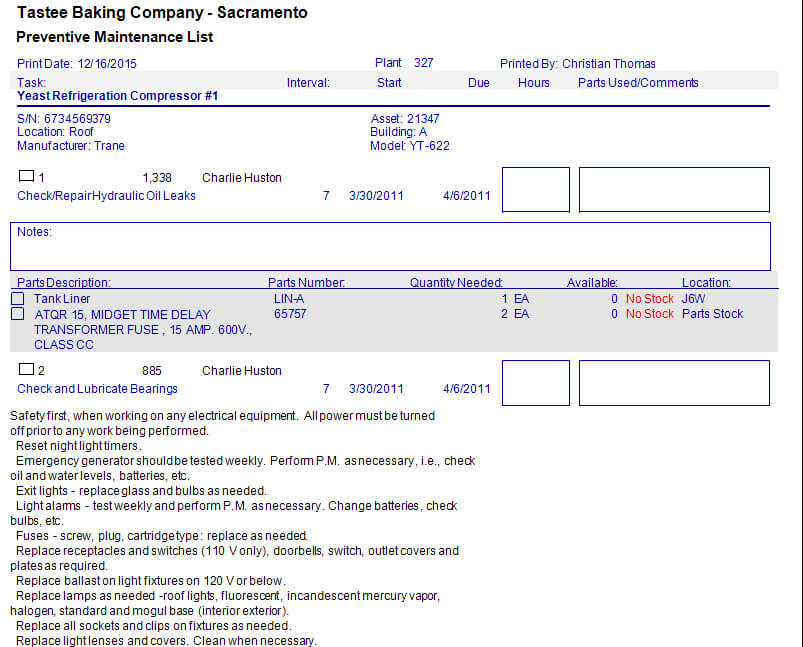
Designing an Effective Preventive Maintenance Program
Designing an effective preventive maintenance program involves the following steps:
- Identify your equipment list.
- Determine equipment run-time requirements.
- Prioritize equipment by function.
- Determine required tasks needed for effective PMs.
- Establish PM interval by calendar day, meter or other interval unit.
- Quantify manpower versus PM task/hour requirements.
- Generate the appropriate preventive maintenance task lists.
Why is a Effective Preventive Maintenance Program Important?
A good preventive maintenance program is important because of the following reasons.
- Effective preventive maintenance reduces unscheduled equipment downtime.
- Lowered downtime interruptions result in a generally smoother production process.
- It is usually less costly to replace worn out parts during preventive maintenance than after an equipment has failed due to lack or PMs.
Identify Your Equipment List
In many cases the maintenance department, or accounting office already has a list of equipment assets. If not then perform an equipment audit. This audit should, at the very least, contain the following data for each equipment item (where feasible):
- Commonly used equipment name
- Asset number
- In use date
- Expected life
- Salvage value
- Replacement cost
Determine Equipment Run-Time Requirements and Equipment Priority
These two points are consolidated because they are so closely related. In some cases run-time requirements vary seasonally.This should be taken into account as it does affect the labor requirements and personnel scheduling
Equipment priority on the other hand usually does not vary. Equipment priority refers to the following points:
- How critical to the process is this equipment item?
- Does the entire process stop if this equipment fails?
- What losses can be expected if this equipment fails?
Determine the Tasks Needed to Perform Preventive Maintenance
Task lists must be carefully designed. Begin by determining what labor resources are available. Unfortunately this is a real constraint that must be considered. Consider needed tasks and task intervals.
Often times tasks and task intervals are simple to determine from an OEM manual or other recommendation. Here are a few other ways to determine tasks and task intervals:
- Consult with other location within your company that use similar equipment under similar conditions.
- Discuss these requirements with the maintenance technicians that have performed maintenance on this equipment in the past.
- Similarly discuss requirements with the personnel that use and rely on the equipment.
- Consider the PM task lists from similar equipment or from historical PM archives.
- Examine equipment downtime and reliability. What is the MTBF (average time between equipment failures) for various reasons?
Create the Preventive Maintenance Task Lists and Balance the Workload
Now that equipment priority, required task lists and intervals are established the next step is to assign the work. This is usually a dynamic process. PM task assignments are determines based upon skills, knowledge of the equipment, technician shift versus equipment run-time shift, equipment availability and current technician workload.
These task lists must be assessed on a regular basis and adjusted as needed. Using the CMMS software reliability analysis, preventive maintenance analysis and work order analysis reporting functions is an essential part of managing these PM tasks lists into the future.